Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Equilibrium of Rigid Body, Translational Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies, Rotational Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies, Toppling of Rigid Bodies, Toppling with Application of Force & Toppling with Linear Velocity etc.
Important Questions on Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
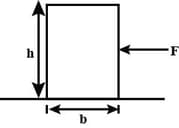
A rectangular block has a square base measuring area and its height is . It moves on a horizontal surface in a direction perpendicular to one of the edges. The coefficient of friction is . It will topple if
Consider a uniform cubical box of side on a rough floor that is to be moved by applying minimum possible force at a point above its centre of mass (see figure). If the coefficient of friction is the maximum possible value of for box not to topple before moving is ________
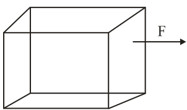
A body is acted upon by two unequal forces in opposite directions, but not in the same line. The effect is that
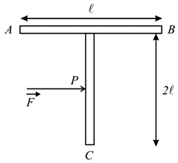
A shaped object with dimensions shown In the figure, is lying on a smooth floor. A force is applied at the point parallel to such that the object has only the translational motion without rotation. Find the location of with respect to
A rod of mass and length is suspended from a vertical wall and kept horizontal by a massless vertical thread as shown. The tension in the thread is,
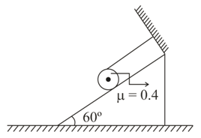
A solid cylinder of mass is wrapped with a string and placed on a rough inclined plane as shown in the fig. Then the frictional force acting between cylinder and plane is
A uniform cube of side a & mass m rests on a rough horizontal table. A horizontal force is applied normal to one of the faces at a point that is directly above the centre of the face, at a height above the base. The minimum value of for which the cube begins to tip about an edge is -----.(assume that cube does not slide).
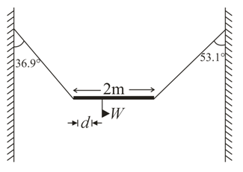
A non-uniform bar of weight is suspended at rest by two strings of negligible weight as shown in Fig. The angles made by the strings with the vertical are and respectively. The bar is long. Calculate the distance of the centre of gravity of the bar from its left end.
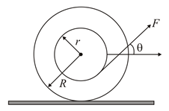
A spool is pulled at an angle with the horizontal on a rough horizontal surface as shown in the figure. If the spool remains at rest, the angle is equal to
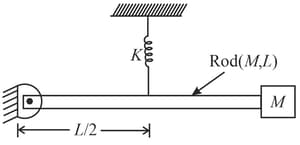
A rod of mass and length is hinged about one end and a particle of mass is attached to its other end. If it is kept horizontal with the help of a spring of spring constant as shown in the figure. Find the extension in spring:-
An engineer is designing a conveyor system for loading lay bales into a wagon. Each bale is 0.25 m wide, 0.50 m high, and 0.80 m long (the dimension perpendicular to the plane of the figure), with mass 30.0 kg. The center of gravity of each bale is at its geometrical center. The coefficient of static friction between a bale and the conveyor belt is 0.60, and the belt moves with constant speed. The angle of the conveyor is slowly increased. At some critical angle a bale will tip (if it doesn't slip first), and at some different critical angle it will slip (if it doesn't tip first).
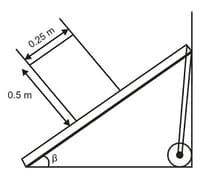
Find the first critical angle (In the same conditions) at which it tips..
A thin uniform rod of mass m and length is moving translationally with acceleration due to two antiparallel forces, as shown. One of the forces is . Find the maximum value of acceleration for which rod may move translationally.
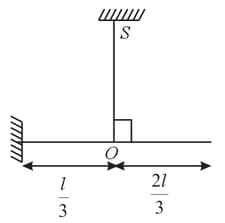
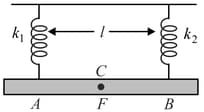
Two light vertical springs with spring constants and are separated by a distance . Their upper ends are fixed to the ceiling and their lower ends to the ends and of a light horizontal rod . A vertical downward force is applied at point on the rod. will remain horizontal in equilibrium if the distance is,
Find the maximum height at which acts, so that sliding and tipping are equally likely to occur.
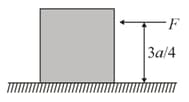
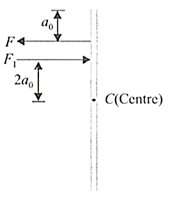
A horizontal force is applied to on the block as shown, which makes it to move with a constant velocity. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is . is applied at height from ground . Distance is the horizontal distance between a point on the bottom face of the block at which the resultant of the friction and normal force act and CG of the block. Find .
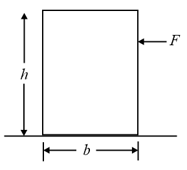
Find the greatest height at which force may be applied to slide the block without tipping over.
A cubical block of mass and side is placed on frictionless horizontal surface. It is hit by a cube at the top to impart impulse in horizontal direction. Minimum impulse(to the nearest integer in ) imparted to topple the block must be greater than –
A cubical block of mass and side is placed on frictionless horizontal surface. It is hit by a cube at the top to impart impulse in horizontal direction. Minimum impulse(to the nearest integer in ) imparted to topple the block must be greater than –
A cubical block of mass and side is placed on frictionless horizontal surface. It is hit by a cube at the top to impart impulse in horizontal direction. Minimum impulse(to the nearest integer in ) imparted to topple the block must be greater than –
A cubical block of mass and side is placed on frictionless horizontal surface. It is hit by a cube at the top to impart impulse in horizontal direction. Minimum impulse(to the nearest integer in ) imparted to topple the block must be greater than –